
O Dhtml é uma verdadeira combinação de tecnologia que resulta uma página Html dinâmica (Dynamic Html) ou em outras palavras com conteúdo que muda automaticamente, ou se baseia na interação com o usuário.
Neste módulo estudaremos o Dhtml associado ao CSS+Javascript
Sua sintaxe é:
document.all.NomeDoSeletor.style.AtributoCSS=ValorCSS
(...)
<nome_da_tag id="NomeDoSeletor"></nome_da_tag>
Observação: quando usamos atributos CSS com hífen tais como:
font-family
font-size
font-style
e outros;
No Dhtml juntamos as duas palavras e a 2ª palavra fica em maiúscula, veja:
fontFamily
fontSize
fontStyle
| Propriedade - CSS | Referência - JavaScript |
|---|---|
| background | background |
| background-attachment | backgroundAttachment |
| background-color | backgroundColor |
| background-image | backgroundImage |
| background-position | backgroundPosition |
| background-repeat | backgroundRepeat |
| border | border |
| border-bottom | borderBottom |
| border-bottom-color | borderBottomColor |
| border-bottom-style | borderBottomStyle |
| border-bottom-width | borderBottomWidth |
| border-color | borderColor |
| border-left | borderLeft |
| border-left-color | borderLeftColor |
| border-left-style | borderLeftStyle |
| border-left-width | borderLeftWidth |
| border-right | borderRight |
| border-right-color | borderRightColor |
| border-right-style | borderRightStyle |
| border-right-width | borderRightWidth |
| border-style | borderStyle |
| border-top | borderTop |
| border-top-color | borderTopColor |
| border-top-style | borderTopStyle |
| border-top-width | borderTopWidth |
| border-width | borderWidth |
| clear | clear |
| clip | clip |
| color | color |
| cursor | cursor |
| display | display |
| filter | filter |
| font | font |
| font-family | fontFamily |
| font-size | fontSize |
| font-variant | fontVariant |
| font-weight | fontWeight |
| height | height |
| left | left |
| letter-spacing | letterSpacing |
| line-height | lineHeight |
| list-style | listStyle |
| list-style-image | listStyleImage |
| list-style-position | listStylePosition |
| list-style-type | listStyleType |
| margin | margin |
| margin-bottom | marginBottom |
| margin-left | marginLeft |
| margin-right | marginRight |
| margin-top | marginTop |
| overflow | overflow |
| padding | padding |
| padding-bottom | paddingBottom |
| padding-left | paddingLeft |
| padding-right | paddingRight |
| padding-top | paddingTop |
| page-break-after | pageBreakAfter |
| page-break-before | pageBreakBefore |
| position | position |
| float | styleFloat |
| text-align | textAlign |
| text-decoration | textDecoration |
| text-decoration: blink | textDecoration = "blink" |
| text-decoration: line-through | textDecoration = "linethrough" |
| text-decoration: none | textDecoration = "none" |
| text-decoration: overline | textDecoration = "overline" |
| text-decoration: underline | textDecoration = "underline" |
| text-indent | textIndent |
| text-transform | textTransform |
| top | top |
| vertical-align | verticalAlign |
| visibility | visibility |
| width | width |
| z-index | zIndex |
Veja um exemplo prático:

<html>
<head>
<title>Exemplo Dhtml </title>
<style type="text/css">
.classe {
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
left: 120px;
font-size:96px;
color: #00ff00;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="seletor" class="classe">Texto</div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Vermelho" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='red'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Azul" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='blue'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Ocultar" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.visibility='hidden'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Exibir" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.visibility='visible'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Direita" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.left=250"><br>
<input type="button" value="Esquerda" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.left=120"><br>
<input type="button" value="Para Baixo" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.top=50"><br>
<input type="button" value="Para Cima" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.top=0"><br>
</form>
Neste exemplo usaremos o atributo CSS font-family
<html>
<head>
<title>Dhtml</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="seletor" style="font-size:30px; color:blue;">Escolhendo o tipo de fonte</div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Arial" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontFamily='Arial'">
<input type="button" value="Verdana" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontFamily='Verdana'">
<input type="button" value="Courier" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontFamily='Courier'">
<input type="button" value="Courier New" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontFamily='Courier New'">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Neste exemplo usaremos o atributo CSS font-size
<html>
<head>
<title>Dhtml</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="seletor" style="font-size:30px; color:blue;">Escolhendo o tamanho da fonte </div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="5px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='5px'">
<input type="button" value="10px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='10px'">
<input type="button" value="15px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='15px'">
<input type="button" value="20px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='20px'">
<input type="button" value="25px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='25px'">
<input type="button" value="30px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='30px'">
<input type="button" value="35px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='35px'">
<input type="button" value="40px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='40px'">
<input type="button" value="45px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='45px'">
<input type="button" value="50px" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.fontSize='50px'">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Neste exemplo usaremos o atributo CSS color:
<html>
<head>
<title>Dhtml</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="seletor" style="font-size:30px; color:blue;">Escolhendo a cor da fonte </div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Verde" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='green'">
<input type="button" value="Amarelo" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='yellow'">
<input type="button" value="Azul" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='Blue'">
<input type="button" value="Vermelho" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='red'">
<input type="button" value="Branco" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='white'">
<input type="button" value="Preto" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.color='black'">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Neste exemplo usaremos o atributo CSS background:
<html>
<head>
<title>Dhtml</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="seletor" style="font-size:30px; color:blue;">Escolhendo a cor de fundo </div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Fundo verde" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.background='green'">
<input type="button" value="Fundo amarelo" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.background='yellow'">
<input type="button" value="Fundo azul" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.background='Blue'">
<input type="button" value="Fundo vermelho" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.background='red'">
<input type="button" value="Fundo branco" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.background='white'">
<input type="button" value="Fundo preto" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.background='black'">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Neste exemplo iremos utilizar o negrito, itálico e o sublinhado para formatar o texto usaremos os atributos CSS:

<html>
<head>
<title>Dhtml</title>
</head>
<script language="javascript">
function negrito() {
if(document.frm_teste.chk_negrito.checked==true){
document.all.seletor.style.fontWeight='bold'
}else {
document.all.seletor.style.fontWeight='normal'
}}
function italico() {
if(document.frm_teste.chk_italico.checked==true){
document.all.seletor.style.fontStyle='italic'
}else {
document.all.seletor.style.fontStyle='normal'
}}
function sublinhado() {
if(document.frm_teste.chk_sublinhado.checked==true){
document.all.seletor.style.textDecoration='underline'
}else {
document.all.seletor.style.textDecoration='none'
}}
</script>
<body>
<div id="seletor" style="font-size:30px; color:blue;">Formatando a Fonte </div>
<form name="frm_teste">
<input type="checkbox" name="chk_negrito" onClick="negrito()">Negrito<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="chk_italico" onClick="italico()">Itálico<br>
<input type="checkbox" name="chk_sublinhado" onClick="sublinhado()">Sublinhado
</form>
</body>
</html>
Para o texto ficar visível ou invisível usaremos o atributo CSS visibility:

<html>
<head>
<title>Dhtml</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="seletor" style="font-size:30px; color:blue;">Visível e invisível</div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Visível" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.visibility='visible'">
<input type="button" value="Invisível" onClick="document.all.seletor.style.visibility='hidden'">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Para posicionar o texto ou para direita, ou para paixo utilizaremos o atributo CSS:
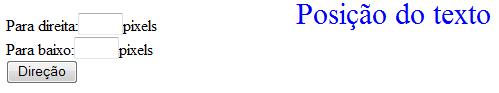
<html>
<head>
<title>Dhtml</title>
</head>
<script language="javascript">
function direcao() {
var direita=document.frm_teste.txt_direita.value
document.all.seletor.style.left=direita
var baixo=document.frm_teste.txt_baixo.value
document.all.seletor.style.top=baixo
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="seletor" style="font-size:30px; color:blue; position:
absolute; top: 0px; left: 300px;">Posição do texto</div>
<form name="frm_teste">
Para direita:<input type="text" name="txt_direita" size="3" maxlength="3">pixels<br>
Para baixo:<input type="text" name="txt_baixo" size="3" maxlength="3">pixels<br>
<input type="button" value="Direção" onClick="direcao()">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Este código indentifica a largura e a altura da imagem

<html>
<head>
<title>Tamanho da imagem</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="imagemx.jpg" id="foto" width="250" height="100"><br>
<script language="javascript">
document.write("Largura da imagem: "+document.all.foto.width)
document.write("<br>")
document.write("Altura da imagem: "+document.all.foto.height)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Com a ajuda do código acima, é possível aumentar e diminuir a figura, veja:

<html>
<head>
<title>Aumentando a imagem</title>
</head>
<script language="javascript">
function aumentar() {
var largura=document.all.foto.width
largura=largura+10
document.all.foto.style.width=largura
var altura=document.all.foto.height
altura=altura+10
document.all.foto.style.height=altura
tamanho(altura, largura)
}
function diminuir() {
var largura=document.all.foto.width
largura=largura-10
document.all.foto.style.width=largura
var altura=document.all.foto.height
altura=altura-10
document.all.foto.style.height=altura
tamanho(altura, largura)
}
function tamanho(altura, largura) {
document.frm_teste.txt_altura.value=altura
document.frm_teste.txt_largura.value=largura
}
</script>
<body>
<form name="frm_teste">
<input type="button" value="Aumentar" onClick="aumentar()">
<input type="button" value="Diminuir" onClick="diminuir()">
<input type="text" name="txt_altura">X
<input type="text" name="txt_largura">
</form>
<img src="imagemx.jpg" id="foto" width="250" height="100"><br>
</body>
</html>
Nos exemplos acima, os códigos Dhtml foram declarado desta forma:
document.all.NomeDoSeletor.style.AtributoCSS=ValorCSS
Mas existem outras duas formas que declara a mesma coisa sendo que de outra maneira:
1) A primeiria forma é excluindo document.all, observe:
NomeDoSeletor.style.AtributoCSS=ValorCSS
2) a segunda forma é incluir o método getElementById em seu código, veja:
document.getElementById("NomeDoSeletor").style.AtributoCSS=ValorCSS
Teste os códigos dos exemplos a segui, também visto anteriormente e compare:

<html>
<head>
<title>Exemplo Dhtml </title>
<style type="text/css">
.classe {
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
left: 120px;
font-size:96px;
color: #00ff00;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="seletor" class="classe">Texto</div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Vermelho" onClick="seletor.style.color='red'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Azul" onClick="seletor.style.color='blue'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Ocultar" onClick="seletor.style.visibility='hidden'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Exibir" onClick="seletor.style.visibility='visible'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Direita" onClick="seletor.style.left=250"><br>
<input type="button" value="Esquerda" onClick="seletor.style.left=120"><br>
<input type="button" value="Para Baixo" onClick="seletor.style.top=50"><br>
<input type="button" value="Para Cima" onClick="seletor.style.top=0"><br>
</form>
<html>
<head>
<title>Exemplo Dhtml </title>
<style type="text/css">
.classe {
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
left: 120px;
font-size:96px;
color: #00ff00;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id="seletor" class="classe">Texto</div>
<form>
<input type="button" value="Vermelho" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.color='red'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Azul" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.color='blue'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Ocultar" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.visibility='hidden'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Exibir" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.visibility='visible'"><br>
<input type="button" value="Direita" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.left=250"><br>
<input type="button" value="Esquerda" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.left=120"><br>
<input type="button" value="Para Baixo" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.top=50"><br>
<input type="button" value="Para Cima" onClick="document.getElementById('seletor').style.top=0"><br>
</form>
Podemos inserir classes CSS inteiras dentro de uma tag, veja no próximo exemplo:

<html>
<head>
<title>onMouseOver</title>
</head>
<style type="text/css">
.on {
font-size:20px;
background:yellow;
color:red;
}
.off {
font-size:16px;
text-decoration:none;
color:black;
}
</style>
<body style="font-family:Arial;">
<ol>
<li><a href="#" class="off" onMouseOver="this.className='on';" onMouseOut="this.className='off';">Item 1</a>
<li><a href="#" class="off" onMouseOver="this.className='on';" onMouseOut="this.className='off';">Item 2</a>
<li><a href="#" class="off" onMouseOver="this.className='on';" onMouseOut="this.className='off';">Item 3</a>
<li><a href="#" class="off" onMouseOver="this.className='on';" onMouseOut="this.className='off';">Item 4</a>
<li><a href="#" class="off" onMouseOver="this.className='on';" onMouseOut="this.className='off';">Item 5</a>
</ol>
</body>
</html>
 foto1.jpg
foto1.jpg
 foto2.jpg
foto2.jpg
 foto3.jpg
foto3.jpg
<html>
<head>
<title>Album</title>
</head>
<body>
<script language="javascript">
if(document.images) {
imagem1 = new Image()
imagem1.src="foto1.jpg"
imagem2 = new Image()
imagem2.src="foto2.jpg"
imagem3 = new Image()
imagem3.src="foto3.jpg"
}
</script>
<img src="foto1.jpg" name="album" width="389" height="291"><br>
<a href="#" onClick="document['album'].src='foto1.jpg'">Foto 1</a>
<a href="#" onClick="document['album'].src='foto2.jpg'">Foto 2</a>
<a href="#" onClick="document['album'].src='foto3.jpg'">Foto 3</a>
</body>
</html>
Descrição: Este script possibilita você colocar imagens em sua página que podem ser movidas de lugar simplesmente arrastando e soltando no lugar desejado.
Obs: Não funciona no Firefox.
<html>
<head>
<title>Teste</title>
<SCRIPT LANGUAGE="JavaScript">
N=(document.all)?0:1;var ob;
function MD(e){
if(N){
ob=document.layers[e.target.name];
X=e.x;
Y=e.y;
return false;
}else{
ob=event.srcElement.parentElement.style;
X=event.offsetX;
Y=event.offsetY;
}
}
function MM(e){
if(ob){
if(N){
ob.moveTo((e.pageX-X),(e.pageY-Y))
}else {
ob.pixelLeft=event.clientX-X+document.body.scrollLeft-2;
ob.pixelTop=event.clientY-Y+document.body.scrollTop-2;
return false;
}
}
}
function MU() {
ob=null
}
if(N){
document.captureEvents(Event.MOUSEDOWN|Event.MOUSEMOVE|Event.MOUSEUP)
}
document.onmousedown=MD;
document.onmousemove=MM;
document.onmouseup=MU
</SCRIPT>
</head>
<body>
<div id="s" style="position:absolute;left:150;top:30;zindex:1">
<img src=erro.gif name="s" width="60" height="56"></div>
<div id="d" style="position:absolute;left:200;top:30;zindex:2">
<img src=flash5.gif name="d" width="151" height="130"></div>
<div id="c" style="position:absolute;left:200;top:80;zindex:3">
<img src=fw.gif name="c" width="36" height="31"></div>
<div id="h" style="position:absolute;left:250;top:80;zindex:4">
<img src=lente.gif name="h" width="57" height="43"></div>
</body>
</html>
Este código é muito útil se você deseja escrever mensagens dentro da página sem mudar nada no código:
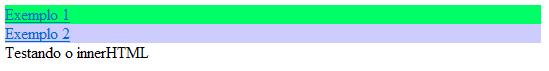
<html>
<head>
<title>Untitled Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background:#00FF66"
onMouseOver="document.getElementById('descricao').innerHTML =
'<b>Inserindo</b> um <u>texto</u> dentro do
<i>Html</i>'"
onMouseOut="document.getElementById('descricao').innerHTML = ''">
<a href="#">Exemplo 1</a>
</div>
<div style="background: #CCCCFF"
onMouseOver="document.getElementById('descricao').innerHTML =
'<u><b>Testando de novo</b></u> o código'"
onMouseOut="document.getElementById('descricao').innerHTML = ''">
<a href="#">Exemplo 2</a>
</div>
<div id="descricao">Testando o innerHTML</div>
</body>
</html>
Exemplo 2: editando texto com innerHTML
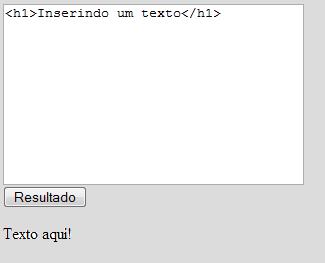
<html>
<head>
<title>Exemplo Dhtml </title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="txt_teste">
<textarea name="texto" cols="100" rows="10"><h1>Inserindo um texto</h1></textarea>
<input type="button" value="Resultado" onClick="id_texto.innerHTML= document.txt_teste.texto.value">
</form>
<div id="id_texto">Texto aqui!</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> function mudaCor() { |